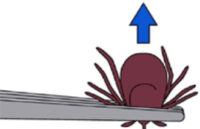
Ticks should be removed promptly. The longer a tick is attached the higher the risk of disease transmission. Ticks can attach to any part of the body but prefer areas such as the armpits, ears, groin, neck and scalp. Tick checks should be preformed routinely after being outdoors.
The tick’s mouthparts have reverse harpoon-like barbs, designed to penetrate and attach to the skin. Ticks secrete a cement-like substance that helps them adhere firmly to their host.
You should NEVER squeeze, crush or puncture the tick’s body because in doing so it may cause the tick to release potential infected fluids into the bite-site. For the same reason, do NOT twist or jerk the tick, do NOT apply petroleum jelly, a hot match, or any other irritants. Irritating the tick may cause it to accelerate the transmission of any diseases it may carry.